FAQ 0840 840 820 (Gratisnummer innerhalb der Schweiz) studentservices@fernuni.ch
Studiengang Master of Science in Artificial Intelligence
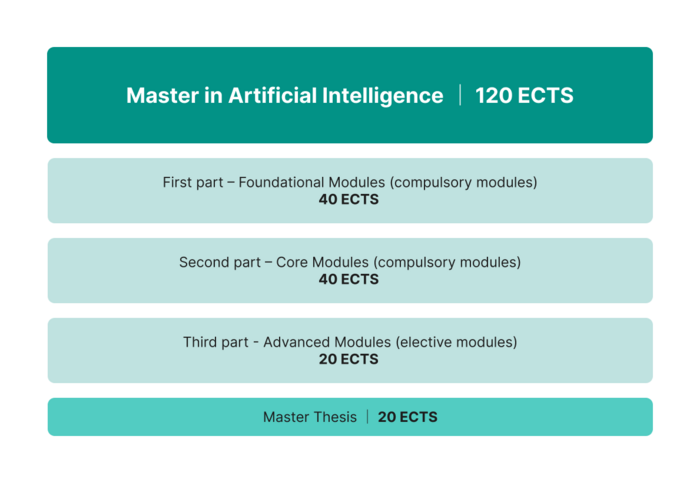
Der Masterstudiengang in KI umfasst 120 ECTS-Punkte. Ein Semester besteht aus zwei Modulen à 10 ECTS, insgesamt also 20 ECTS pro Semester. In der Regel dauert der Erwerb dieser ECTS 3 Jahre.
Der Studienplan ist so konzipiert, dass er eine starke theoretische und praktische Grundlage bietet und gleichzeitig einen flexiblen Spezialisierungsweg ermöglicht.
Die Module sind in drei Kategorien unterteilt: Grundlagen-, Kern- und Vertiefungsmodule.
Grundlagenmodule (Semester 1 und 2)
Diese obligatorischen Module (M01–M04) vermitteln die wesentlichen Grundlagen in Informatik, Mathematik, maschinellem Lernen und Deep Learning, die für das Verständnis moderner KI erforderlich sind.
Kernmodule (Semester 3 und 4)
Die Kernmodule vermitteln den Studierenden umfassende Kenntnisse der Theorie und Praxis moderner KI. Drei Module befassen sich mit den wichtigsten KI-Modalitäten: Modul M05 konzentriert sich auf Vision (z. B. Bilderkennung und -generierung), Modul M07 auf Text (z. B. Large Language Models) und Modul M08 auf Audio (z. B. Spracherkennung und -generierung). Modul M06 vertieft fortgeschrittene allgemeine Deep-Learning-Techniken, wie etwa das Reinforcement Learning. Diese Module sind obligatorisch.
Vertiefungsmodule (Semester 5 und 6)
Die Vertiefungsmodule sind Wahlmodule, die spezifische Teilbereiche der modernen KI vertieft behandeln und die Studierenden zu Experten in diesen Bereichen ausbilden. Die Studierenden gestalten ihr Studium individuell, indem sie zwei Module entsprechend ihren Interessen und beruflichen Zielen auswählen. Die Module können in beliebiger Reihenfolge belegt werden, sofern dies mit dem Studienplan vereinbar ist, und können parallel zur Masterarbeit (M13) absolviert werden.
Die Masterarbeit bildet den Abschluss des Studienprogramms. Die Studierenden nutzen die erworbenen Kenntnisse, um ein Projekt im Bereich der Künstlichen Intelligenz durchzuführen. Sie wird entweder (a) in den letzten beiden Semestern, (b) im letzten Semester oder (c) im vorletzten Semester absolviert, abhängig von den gewählten Wahlmodulen.
Pflichtmodul(e)
This course provides a concise and practical introduction to the key mathematical concepts that form the backbone of modern machine learning and AI. It covers linear algebra, probability theory and basic optimization, with numerous examples illustrating their relevance for AI. The course equips students with the intuition and tools necessary to understand, analyze, and implement AI algorithms.
• Linear algebra:
- Vector spaces, bases, subspaces
- Rank, Invertibility
- Eigenvalues, eigenvectors, spectral theorem
- Linear regression
- Singular Value Decomposition and Principal Component Analysis
• Probability:
- Discrete Distributions
- Continuous distributions / densities
- Independence, correlation
- Multivariate normal distribution
- Conditional probability, Bayes theorem
• Multivariate calculus
This course provides a broad introduction to the core concepts in computer science that support modern machine learning and AI workflows. The course covers fundamental principles of programming, algorithms and computational complexity, computer architecture, operating systems, databases, and essential software engineering practices, equipping students with the practical skills and technical foundation needed to build and deploy AI systems effectively.
• Software design and basics of computer programming (data structures, classes, functional programming, boolean logic, etc.)
• Computational complexity
• Algorithms (recursion, sorting, randomization, tree search, parallelism and distributed computing)
Professor/in

This course introduces the core statistical principles and learning algorithms that underpin modern machine learning approaches. Bridging theory and practice, it explores how uncertainty, data structure, and model complexity interact in the design and evaluation of predictive systems. Emphasis is placed on developing both a conceptual understanding and the practical intuition needed to apply machine learning methods thoughtfully and effectively.
• Statistics: estimation, confidence intervals, maximum likelihood estimation, hypothesis testing, Bayesian models
• Machine learning:
- Basics: types of problems (regression, classification, probability estimation), data representation, generalization and bias-variance dilemma
- Linear models (Linear regression, Logistic regression)
- Non-linear models, Support Vector Machines and kernel methods
- Dimensionality reduction & Visualization methods
- Bayesian models
- Clustering algorithms
Dozent/in
This course is an in-depth exploration of the deep learning architectures and foundation models that have revolutionized artificial intelligence. Students will study core neural network architectures and optimization techniques, including architectures for generative models. Special emphasis is placed on transformers and large-scale pre-trained models across various modalities, including natural language processing and computer vision. Practical sessions provide hands-on experience with modern tools and frameworks to develop and fine-tune deep learning models for real-world applications.
• Architectures, training and optimization
• Generative AI
• Transformers
• Foundation models
Dozent/in
This course is an introduction to the fundamental concepts and techniques of computer vision. It covers essential image processing methods and core vision tasks such as classification, detection, segmentation, and tracking. Students will gain a solid understanding of the principles behind visual perception by machines and develop practical skills to build and evaluate vision systems.
• Basics of image processing
• Tasks: Classification, detection, segmentation, tracking, generation (diffusion models)
• Vision architectures: vision transformers, vision language models, etc.
• Advanced topics: multidimensional computer vision (3D vision & geometry, video etc.)
Dozent/in
This course delves into advanced topics in deep learning, including reinforcement learning, learning on complex data structures such as graphs, and techniques for adapting models to new domains and limited data. Students will deepen their understanding of cutting-edge methods and their applications with a focus on recent developments in AI research and applications.
• Reinforcement learning
• Machine Learning on networks (e.g. graph-neural networks)
• Finetuning, domain adaptation
• Additional topics, e.g.
- Multi-GPU training
- Advanced training algorithms (Muon, SOAP, etc.)
- Quantization
Dozent/in
This course covers advanced techniques in natural language processing (NLP), focusing on the powerful large language models that shape today’s AI landscape. Students will explore how machines understand and generate human language, learn methods to train and fine-tune these models, and discuss important practical challenges. In hands-on practical sessions students will work directly with the latest tools and technologies used in cutting-edge NLP applications.
• Basics of Natural Language Processing (data and levels of representation).
• Tasks (selection): syntactic parsing, semantic role labelling, machine translation, information extraction, sentiment analysis, dialogue.
• Architectures: transformers, BERT, GPTs, small language models, RNNs, LSTMs.
• Advanced topics: low-resource languages and multilingualism, reasoning models, conversational and dialogue models.
Dozent/in
This course covers advanced concepts in speech and audio processing, focusing on how machines analyze, interpret, and generate audio signals. Students will study fundamental techniques for speech recognition, audio feature extraction, and sound synthesis, alongside modern approaches to handling real-world audio data. Through hands-on practical sessions, students will gain experience working with state-of-the-art tools and methods used in speech and audio technologies :
• Basics of speech science: speech production, audio perception, phonetics
• Signal processing and feature engineering: audio acquisition, time domain processing, frequency domain processing, audio analysis-synthesis, knowledge-driven feature representations, data-driven feature representations
• Speech processing tasks: speech activity detection, speech enhancement, speech and audio coding, speech recognition, speech synthesis, speaker recognition, paralinguistic speech processing, deep fake detection
• Machine learning for speech processing: statistical formulation (application of Bayes' rule and hypothesis testing), neural architectures (MLP, RNN, CNN, transformers, LSTM), Gaussians/k-means/Gaussian mixture models, k-NN, SVM, Random Forest, Adaboost, hidden Markov models, Discrete Markov models, CTC, RNN-T, self-supervised learning
• Advanced topics : spoken language processing (speech + NLP), Bimodal (audio-visual) speech processing
Dozent/in
The master's thesis gives students the opportunity to apply the knowledge and skills acquired throughout their studies in an in-depth independent project. The thesis may take the form of a traditional academic research project, or an applied project carried out in collaboration with an industry partner (subject to approval by the programme director of the Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science).
Dozent/in
Elective modules (students choose 2 out of 4)
This course introduces the concept of Agentic AI, focusing on the design of intelligent systems capable of autonomous, goal-directed behaviour. Students will explore what it means for an AI system to act as an “agent”, i.e. to interact with its environment, make decisions, and adapt over time. Through a mix of theory and practical work, students will gain a foundational understanding of agent-based thinking in AI and its relevance to real-world applications.
• Multi-agent systems
• Model Context Protocol (MCP)
• Evaluation
• Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
• Memory (prompting and conversation history), safety, alignment
This course explores the application of machine learning and AI techniques to problems in finance and insurance. Students will learn how data-driven models can support decision-making in areas such as risk assessment, fraud detection, pricing, portfolio optimization, and forecasting.
The course combines theoretical foundations with practical case studies, allowing students to understand both the opportunities and limitations of AI in highly regulated, data-sensitive industries.
This course introduces the fundamentals of robotics and autonomous systems, focusing on how machines can perceive their environment, make decisions, and act independently. Students will gain a foundational understanding of how robots operate in real-world environments and the challenges involved in designing truly autonomous systems.
• Intro to robotics (sensors, actuators, ROS, etc.)
• Representation of robot movements
• Optimal control
• Human-robot interaction (interactions design, user interfaces, human-robot collaboration, and evaluation).
This module will detail key methods of design thinking that help you build products that stand out in an environment where AI is enabling quick technical implementation of prototypes and products. By the end of this module, you will be able to design, implement, and evaluate prototypes that are aligned with users' needs. Topics covered include:
• History and principles of Human-Computer Interaction
• Design thinking and methods of design (double diamond, iterative prototyping, user journeys, user personas)
• AI-powered design and prototyping
• Evaluation methods: Quantitative (NHST, Bayesian methods), qualitative (interviews, thematic analysis), and mixed-methods (exploratory, explanatory).
Noch Fragen?
Unsere Student Manager sind für Sie da!